Drinking water is one of the most important human needs and directly linked with our survival. An average human drinks about 1.5 liter water per day. Even though the water is abundantly available on our planet but about 98% water is saline and not drinkable only about 2 % water can be used for drinking. Due to industrial growth and developments in last century, ground fresh water is polluting at alarming rates. Especially in under development countries, lack of regulations and awareness is complicating the problem. Moreover, many areas naturally lack the pure drinking water. Lack of pure drinking water is causing numerous health problems especially in children. Localized solution is to install water treatment plants
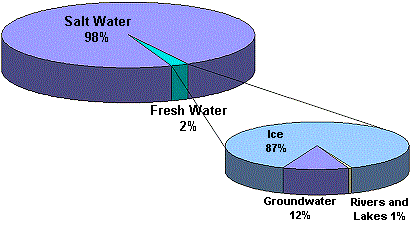
Drinking water treatment plants:
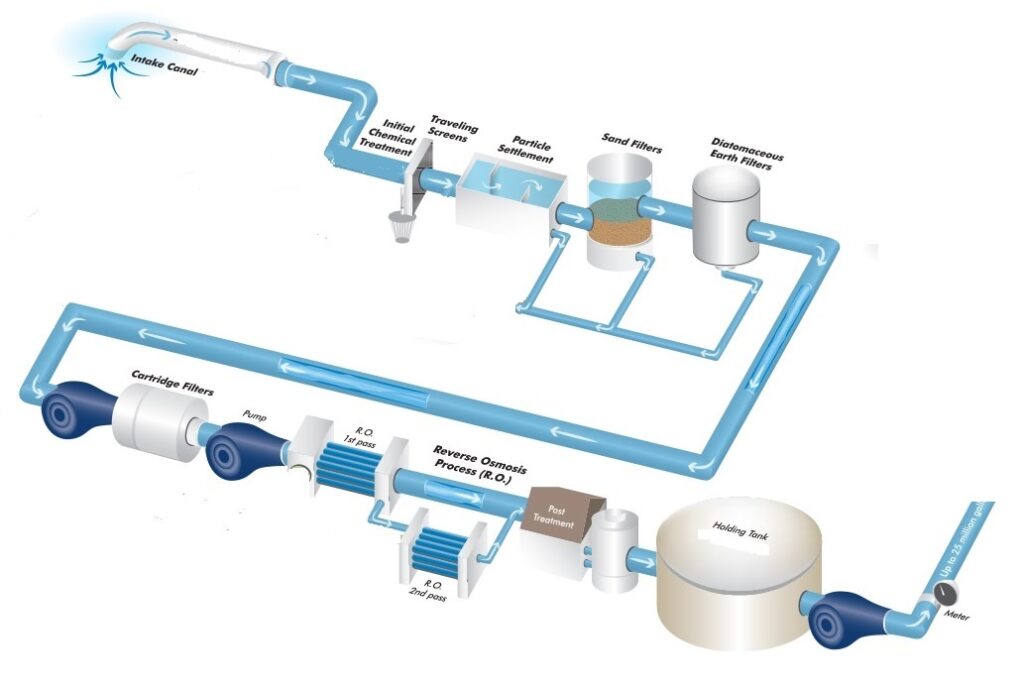
Drinking water treatment plants are used to remove solids, chemical impurities and organic matter which are harmful to the humans and cause different diseases. Water treatment requirements depend upon the quality of water which enters the process. For example, water from river, sea and lakes requires more treatment as compare to ground water.
Here we will briefly explain the process and major components of a drinking water treatment plant with feed from ground water.
Types of Impurities:
In ground water following types of impurities are generally present
- Heavy Metals (i.e. Lead, Copper, Mercury, Arsenic and Cadmium etc.)
- Chemical Impurities (i.e. Nitrates, Fluorides, Chlorine etc.)
- Micro Organisms (i.e. Bacteria, Viruses, Parasites etc.)
Major Steps of Water Treatment:
Major stages of water treatment plant are mentioned below while selection and sizing of appropriate types depends upon the type and concentration of impurities available in feed water
Coagulation: This process is used to remove the dirt and other solid particles in start of water treatment plant. Different coagulating agents are added in water which attract the dirt and solid particles and make floc. It settles down under the water and can be removed. Alum is one the coagulating agents and generally used in houses for cleaning the dirty water.
Filtration: In filtration, water is passed through different filtration media. Common filtration media includes sand, gravels and charcoal
RO membrane System: It is the heart of the drinking water treatment plant. Membrane system works on the principle of Reverse Osmosis and capable of removing majority of molecules bigger then water molecule. RO membranes can removes a wide verity of dissolved salts, metals and other small molecules which can escape from conventional filtration system. In membrane system, membrane element is placed in a pressure shell and water is passed at high pressure. Membrane allows the passing of water molecules and bigger molecules are collected as permeate. Membrane outlet water is very pure and without any healthy nutrients so may not be directly used for drinking without further processing

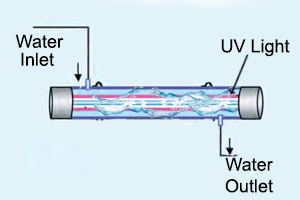
UV treatment: UV treatment is an effective way of removing the bacteria from water. Ultraviolet rays in UV treatment system attack the microorganism resent in the water and destroy their DNA thus restricting their reproduction. UV system can kill 99% of water born harmful pathogens without any need of chemicals thus it is considered as safest and cost effective method.
TDS Control Unit: This unit is used for mixing of membrane unit outlet water with potable water to achieve acceptable total dissolved solids.
Specialized treatments: Many different specialized treatment processes are used depending upon the presence of impurities. One of them is Arsenic removal unit. Arsenic being carcinogenic is very harmful for human consumption. Different techniques are available for Arsenic removal including Ion Exchange, Sorption filtration process, Coagulation process, Oxidation process.
Other auxiliary components include water pumps, storage tank, instrumentation, quality monitoring meters etc.
Required Drinking water Quality:
World Health Organization (WHO) and other international agencies has developed and issued drinking water quality documents indicating limits of all major components. Below table shows generally acceptable water quality parameters
| Parameter | Units | Acceptable/ Desirable Limit |
| Color | Hazen Unit | 5 |
| PH | — | 6.5 – 8.5 |
| TDS | mg/liter | 300-600 |
| Conductivity | µS cm | 2500 |
| Hardness (as CaCO3) | Mg/liter | 75-300 |
| Arsenic | μg/liter | <10 |
| Total Iron | ppm | 0.3 |